
In the evolving landscape of healthcare management, accurate age calculation has become a cornerstone for maintaining precise medical records. The implementation of age calculators in healthcare settings has revolutionized how medical professionals track patient data, assess health risks, and develop personalized treatment plans. This comprehensive guide explores how to effectively use an age calculator for medical and health records, with a particular focus on biological age calculation.
Understanding the Difference Between Chronological and Biological Age
Before diving into the practical applications of age calculators in healthcare, it's essential to understand the fundamental distinction between chronological and biological age.
Chronological Age refers to the time that has passed since birth, measured in years, months, days, and sometimes even hours. This is the standard age measurement that appears in most medical records and official documents.
Biological Age, on the other hand, reflects the physiological state of your body compared to standard age norms. It considers various biomarkers, lifestyle factors, and health indicators to determine how well your body is functioning relative to your chronological age.
In medical settings, understanding both measures provides a more comprehensive picture of a patient's health status. While chronological age is straightforward to calculate, biological age requires more sophisticated tools and consideration of multiple health parameters.
The Importance of Accurate Age Calculation in Medical Records
Healthcare professionals rely on precise age data for numerous critical functions:
- Medication Dosing: Many drug dosages are age-dependent, especially for pediatric and geriatric patients.
- Developmental Assessment: For children, age calculation down to the day can be crucial for evaluating developmental milestones.
- Age-Related Screening: Recommendations for preventive screenings like mammograms, colonoscopies, and prostate exams are based on age.
- Research and Epidemiology: Age-stratified data is essential for medical research and population health studies.
- Insurance and Billing: Accurate age information ensures proper coverage and billing.
Errors in age calculation, even minor ones, can potentially lead to improper treatment protocols or missed screening opportunities. This underscores the need for reliable age calculation tools in healthcare settings.
Basic Features of Medical Age Calculators
Modern medical age calculators offer a range of functionality specifically designed for healthcare applications:
Chronological Age Calculation
The foundation of any medical age calculator is the ability to accurately compute the time between two dates:
- Date of Birth to Current Date: Calculates a patient's current age
- Date of Birth to Specific Date: Determines a patient's age at a particular point in time, such as the date of an examination or procedure
- Between Any Two Dates: Measures time intervals between medical events
These calculations typically provide results in multiple formats:
- Years, months, and days
- Decimal years (e.g., 42.7 years)
- Total months or weeks (for pediatric applications)
- Days (for acute care settings)
Age Verification for Medical Records
Electronic health record (EHR) systems incorporate age calculation tools to:
- Verify patient identity
- Flag potential record errors
- Ensure compliance with age-related regulations
- Track age-dependent health metrics
Healthcare facilities often integrate these calculators directly into their EHR workflows to streamline documentation and reduce the potential for manual calculation errors.
Advanced Applications: Calculating Biological Age
While chronological age calculation is straightforward, biological age determination involves more complex algorithms and multiple inputs. Modern medical age calculators increasingly include biological age assessment capabilities, which can provide valuable insights for preventive care and personalized medicine.
Biomarkers Used in Biological Age Calculation
Comprehensive biological age calculators may incorporate various biomarkers:
- Physiological Measurements:
- Blood pressure
- Resting heart rate
- Lung capacity
- Body mass index (BMI)
- Waist-to-hip ratio
- Laboratory Values:
- Complete blood count
- Fasting glucose
- Lipid profile
- Inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein, IL-6)
- Hormonal levels
- Functional Assessments:
- Grip strength
- Walking speed
- Balance tests
- Cognitive function
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking status
- Alcohol consumption
- Physical activity levels
- Sleep quality
- Nutrition
- Genetic and Molecular Markers:
- Telomere length
- DNA methylation patterns
- Gene expression profiles
By integrating these diverse data points, advanced age calculators can generate a biological age estimate that may differ significantly from a patient's chronological age, providing a more nuanced view of their overall health status.
How to Implement Age Calculation in Healthcare Settings
Integration with Electronic Health Records
Modern healthcare facilities benefit from age calculators that directly integrate with their EHR systems. Implementation typically follows these steps:
- Select Compatible Software: Choose an age calculator that interfaces with your existing EHR system
- Configure Settings: Set up default parameters (units, display formats, etc.)
- Train Staff: Ensure all healthcare professionals understand how to use the calculator
- Establish Protocols: Create guidelines for when and how to document age calculations
- Regular Updates: Maintain the software to ensure continued accuracy and compatibility
Best Practices for Age Computation in Medical Contexts
To maximize the benefits of age calculators in healthcare:
- Use Consistent Methods: Standardize calculation approaches across your organization
- Document Methodology: Record which calculator and settings were used
- Consider Cultural Variations: Be aware of different age-counting systems across cultures
- Verify Critical Calculations: Double-check age-based decisions that significantly impact treatment
- Maintain Precision: Use the highest precision available when age impacts dosing or developmental assessment
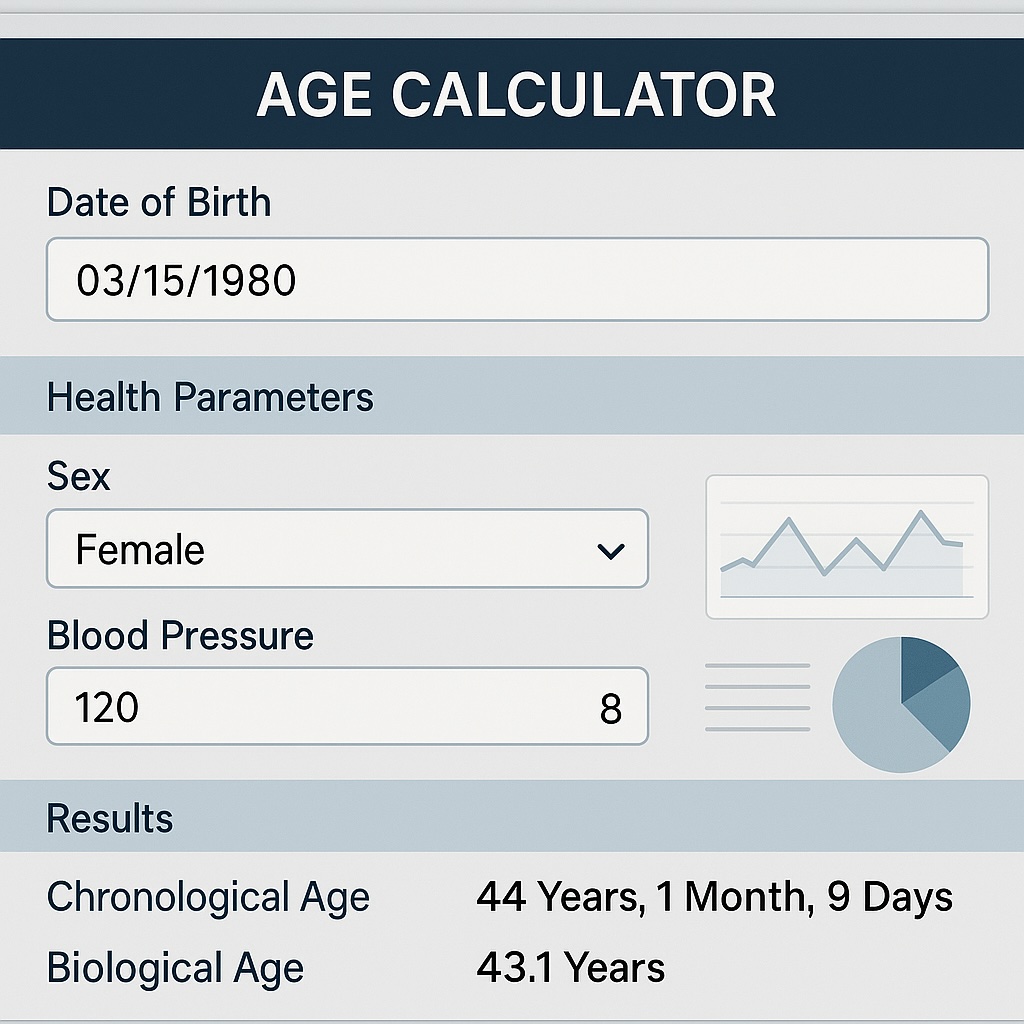
Step-by-Step Guide to Using an Age Calculator for Patient Records
For Basic Chronological Age Calculation:
- Access the Calculator: Open your EHR-integrated calculator or a standalone medical age calculation tool
- Enter Birth Information: Input the patient's date of birth
- Set Reference Date: Enter today's date or a specific reference date
- Review Results: Verify the calculated age is displayed in the required format
- Document: Record the result in the appropriate section of the patient's medical record
- Recalculate as Needed: Update calculations for future visits or specific reference points
For Biological Age Assessment:
- Gather Required Data: Collect necessary biomarkers and health metrics
- Input Values: Enter the collected data into the biological age calculator
- Run the Calculation: Process the information using the calculator's algorithm
- Interpret Results: Compare biological age with chronological age
- Discuss with Patient: Explain the significance of any discrepancies
- Develop Interventions: Create health plans to address problematic areas
- Monitor Changes: Track biological age over time to assess intervention effectiveness

Benefits of Using Digital Age Calculators in Healthcare
For Healthcare Providers:
- Increased Accuracy: Eliminates manual calculation errors
- Time Efficiency: Reduces the time spent on administrative tasks
- Standardization: Ensures consistent age calculation across departments
- Better Decision Support: Provides immediate age-based guidance for clinical decisions
- Enhanced Research Capabilities: Facilitates age-stratified data analysis
For Patients:
- Personalized Care: Supports tailored treatment based on both chronological and biological age
- Preventive Focus: Identifies age-related risk factors earlier
- Motivation for Improvement: Provides tangible metrics for lifestyle modifications
- Better Understanding: Helps patients comprehend age-related health recommendations
- Health Ownership: Encourages greater engagement in personal health management
Case Studies: Age Calculation in Clinical Practice
Pediatric Growth Assessment
Pediatricians frequently use age calculators to precisely determine a child's age in months, weeks, and days when assessing growth and development. This level of precision is essential because developmental milestones can change rapidly, especially in infants and toddlers.
Example: A premature infant born at 32 weeks gestation requires "corrected age" calculations for accurate developmental assessment. Age calculators designed for pediatric use can automatically adjust for prematurity, ensuring appropriate growth curve plotting and milestone evaluation.
Geriatric Care Planning
In geriatric medicine, the gap between chronological and biological age often widens. Geriatricians use comprehensive age calculators to determine which patients may need more aggressive preventive interventions despite their chronological age.
Example: A 75-year-old patient with a calculated biological age of 65 might be considered for treatments typically reserved for younger patients, while a 65-year-old with a biological age of 75 might require a more conservative approach.
Clinical Research Participant Selection
Research studies often have strict age criteria for participant inclusion. Advanced age calculators ensure accurate subject selection and stratification.
Example: A clinical trial studying a new osteoporosis treatment might include postmenopausal women between 55-70 years old. Precise age calculation ensures appropriate participant selection and valid results.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Data Privacy Concerns
Challenge: Age calculators may process sensitive health information, raising privacy concerns.
Solution:
- Use HIPAA-compliant tools
- Implement strong data encryption
- Limit access to authorized personnel
- Conduct regular security audits
- Anonymize data when possible
Cultural Age Calculation Differences
Challenge: Different cultures may have varying traditions for age calculation.
Solution:
- Document traditional age alongside standard medical age
- Train staff on cultural variations
- Use standardized medical age for clinical decisions while respecting cultural preferences
- Provide clear explanations to patients about which system is being used
Technical Integration Issues
Challenge: Compatibility problems between age calculators and existing EHR systems.
Solution:
- Conduct thorough testing before full implementation
- Work with vendors who offer robust integration support
- Develop backup calculation procedures
- Implement regular validation checks
- Update systems as needed
Future Trends in Medical Age Calculation
The field of medical age calculation continues to evolve, with several promising developments on the horizon:
AI-Enhanced Biological Age Assessment
Artificial intelligence algorithms are increasingly being used to analyze complex patterns of biomarkers, providing more nuanced biological age calculations. These systems can identify subtle correlations that might be missed by traditional statistical methods.
Wearable Integration
The integration of age calculators with data from wearable devices allows for continuous monitoring of factors that influence biological age, such as activity levels, sleep patterns, and heart rate variability.
Personalized Aging Trajectories
Rather than providing a single biological age number, future calculators may offer personalized aging trajectories across different body systems, recognizing that organs and functions may age at different rates within the same individual.
Epigenetic Clocks
Advanced biological age calculators increasingly incorporate epigenetic data, particularly DNA methylation patterns, which have shown remarkable accuracy in predicting age-related health outcomes.

Conclusion
Age calculators have evolved from simple date-difference tools to sophisticated instruments essential for modern healthcare delivery. Their implementation in medical and health record systems enhances accuracy, improves clinical decision-making, and supports personalized medicine initiatives.
By understanding how to properly use age calculators for both chronological and biological age assessment, healthcare professionals can provide more precise, age-appropriate care while potentially identifying health risks before they develop into serious conditions.
As biological age calculation becomes increasingly refined, we can expect these tools to play an even more central role in preventive medicine and personalized healthcare. For healthcare facilities and professionals still relying on manual calculations, transitioning to dedicated medical age calculators represents a small implementation step that can yield significant improvements in patient care and operational efficiency.
Whether used for medication dosing, developmental assessment, or comprehensive health evaluation, age calculators stand as valuable instruments in the healthcare professional's digital toolkit—tools that, when properly utilized, contribute to better patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare delivery.
Try Our Medical Age Calculator Today
Ready to experience the benefits of accurate age calculation in your healthcare practice? Our Age Calculator tool is specifically designed for medical professionals and health record management.
Get started with our Medical Age Calculator today and transform how you track and utilize patient age data in your practice.





