คู่มือเชิงลึกในการสร้างเครื่องคิดเลขเรขาคณิตแบบโต้ตอบของคุณเองโดยใช้ JavaScript พร้อมด้วยการคำนวณพื้นที่สำหรับรูปหลายเหลี่ยมที่เรียบง่ายและซับซ้อน
บทนำ: ทำไมต้องสร้างเครื่องคิดเลขเรขาคณิต? การคำนวณรูปทรงเรขาคณิตเป็นรากฐานของแอพพลิเคชั่นในโลกแห่งความเป็นจริงจำนวนมากตั้งแต่การสำรวจที่ดินและสถาปัตยกรรมไปจนถึงการพัฒนาเกมและระบบข้อมูลทางภูมิศาสตร์ในฐานะนักพัฒนาเรามักจะต้องการเครื่องมือที่เชื่อถือได้ในการคำนวณพื้นที่ของรูปร่างที่หลากหลายในขณะที่มีเครื่องคิดเลขออนไลน์จำนวนมากสร้างข้อเสนอของคุณเอง:
การปรับแต่งให้สมบูรณ์เพื่อให้เหมาะกับข้อกำหนดโครงการเฉพาะของคุณ ความยืดหยุ่นในการรวมเข้ากับเว็บแอปพลิเคชันที่มีอยู่ของคุณ โอกาสในการเรียนรู้เพื่อทำความเข้าใจการประสานงานเรขาคณิตและการคิดอัลกอริทึม การเพิ่มพอร์ตโฟลิโอเพื่อแสดงทักษะ JavaScript ของคุณ ในบทช่วยสอนที่ครอบคลุมนี้เราจะเดินผ่านกระบวนการสร้างเครื่องคิดเลขพื้นที่เรขาคณิตที่ทรงพลังและมีประสิทธิภาพโดยใช้ JavaScriptในตอนท้ายคุณจะมีเว็บแอปพลิเคชันที่ใช้งานได้อย่างสมบูรณ์ซึ่งคำนวณพื้นที่ของรูปหลายเหลี่ยมที่เรียบง่ายและซับซ้อนโดยใช้เรขาคณิตพิกัด
สิ่งที่เราจะสร้าง เครื่องคิดเลขเรขาคณิตของเราจะ:
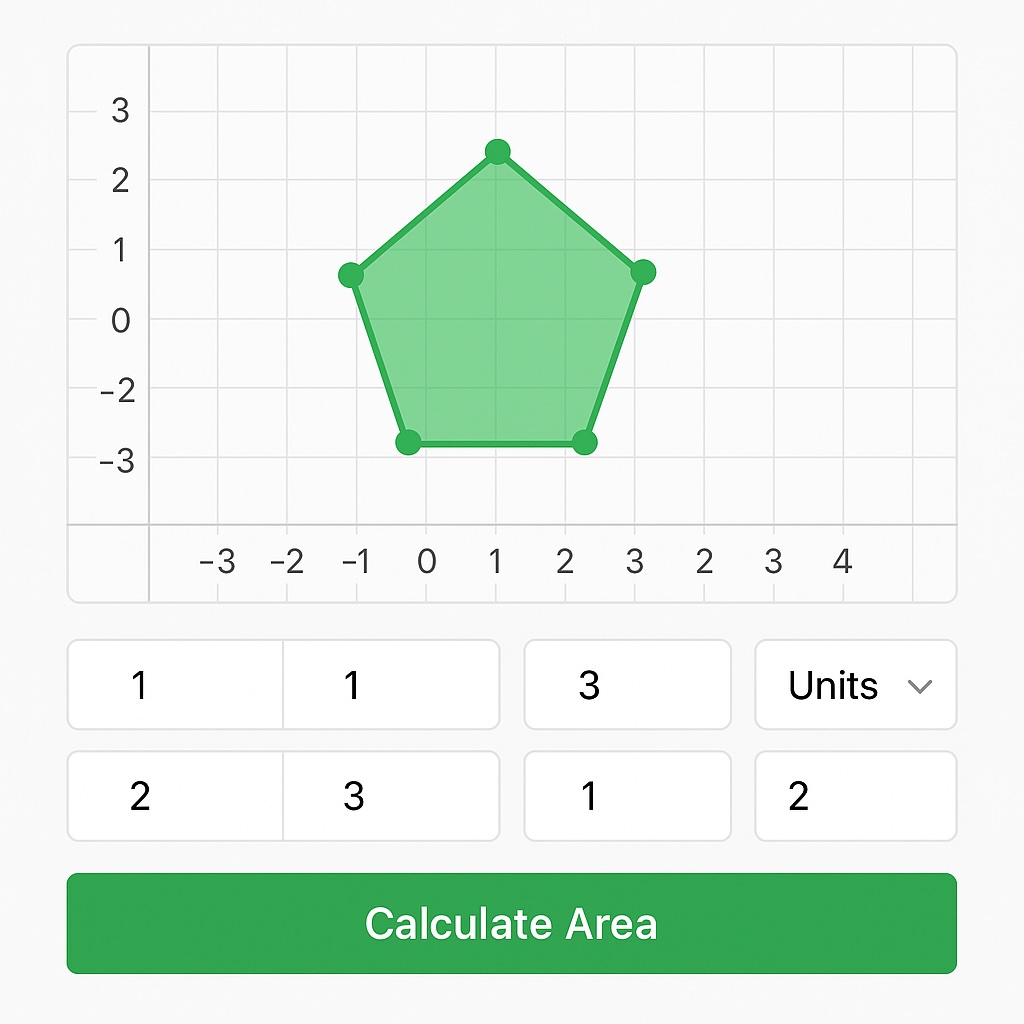
อนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้ป้อนพิกัดรูปหลายเหลี่ยมผ่านอินเทอร์เฟซที่ใช้งานง่าย คำนวณพื้นที่สำหรับทั้งรูปหลายเหลี่ยมปกติและผิดปกติ รองรับหน่วยวัดหลายหน่วย เห็นภาพรูปร่างโดยใช้ HTML Canvas ให้ผลลัพธ์ที่ชัดเจนและแม่นยำด้วยการปัดเศษที่เหมาะสม ทำงานในเบราว์เซอร์และอุปกรณ์ที่สำคัญทั้งหมด ตัวอย่างของเครื่องคำนวณพื้นที่เรขาคณิตจาวาสคริปต์สุดท้ายของเราพร้อมอินพุตรูปหลายเหลี่ยมแบบโต้ตอบ
ข้อกำหนดเบื้องต้น ในการติดตามพร้อมกับบทช่วยสอนนี้คุณควรมี:
ความเข้าใจพื้นฐานของ HTML, CSS และ JavaScript ความคุ้นเคยกับการจัดการ DOM ตัวแก้ไขข้อความหรือ IDE (รหัสเทียบกับข้อความประเสริฐ ฯลฯ ) เว็บเบราว์เซอร์ที่ทันสมัย ทางเลือก: การทำความเข้าใจพื้นฐานเรขาคณิตพิกัด
ทำความเข้าใจคณิตศาสตร์ที่อยู่เบื้องหลังการคำนวณพื้นที่ ก่อนที่จะดำน้ำเป็นรหัสเรามาทำความเข้าใจหลักการทางคณิตศาสตร์ที่ให้พลังงานกับเครื่องคิดเลขเรขาคณิตของเรา
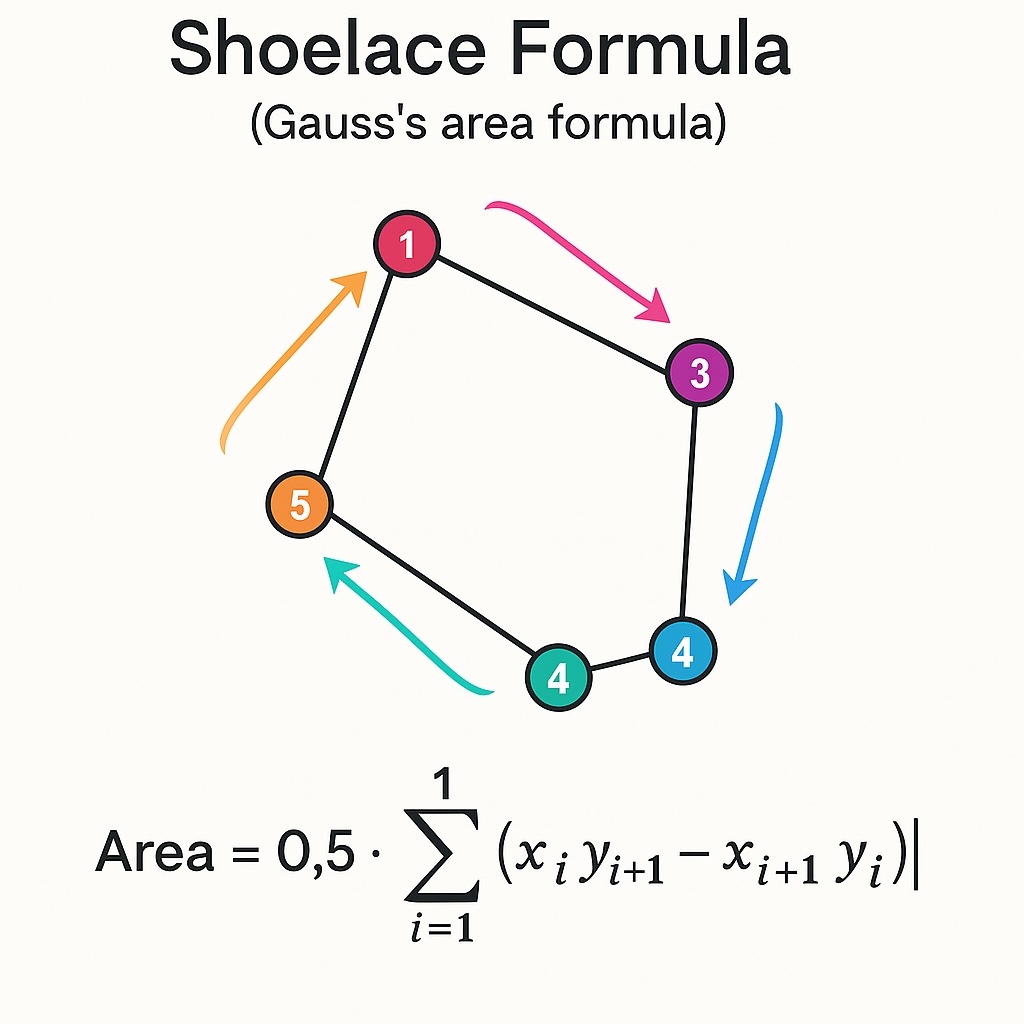
สูตรเชือกผูกรองเท้าสำหรับพื้นที่รูปหลายเหลี่ยม สำหรับการคำนวณพื้นที่ของรูปหลายเหลี่ยมใด ๆ (ปกติหรือผิดปกติ) เราจะใช้สูตรเชือกผูกรองเท้าหรือที่เรียกว่าสูตรของสำรวจหรือสูตรพื้นที่ของเกาส์อัลกอริทึมที่ทรงพลังนี้ใช้งานได้กับรูปหลายเหลี่ยมใด ๆ ที่กำหนดโดยจุดยอดของมันโดยไม่คำนึงถึงความซับซ้อนของรูปร่าง
สูตรแสดงเป็น:
Area = 0.5 * |∑(x_i * y_(i+1) - x_(i+1) * y_i)|
ที่ไหน:
x_i and y_i are the coordinates of the i-th vertexสูตรคำนวณครึ่งผลรวมของผลิตภัณฑ์ข้ามของจุดยอดที่อยู่ติดกัน ค่าสัมบูรณ์ทำให้มั่นใจได้ว่าพื้นที่เชิงบวก สูตรนี้ทำงานโดย "เดิน" รอบ ๆ ปริมณฑลของรูปหลายเหลี่ยมคำนวณผลิตภัณฑ์ข้ามระหว่างจุดต่อเนื่องเมื่อเราสรุปสิ่งเหล่านี้และหารด้วย 2 เราจะได้พื้นที่ของรูปหลายเหลี่ยม
การตั้งค่าโครงการ เริ่มต้นด้วยการตั้งค่าโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของเครื่องคิดเลขเรขาคณิตของเรา:
โครงสร้าง HTML Create a new file named index.html with the following structure:
Copy <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Geometry Area Calculator</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="calculator-container">
<h2>Geometry Area Calculator</h2>
<div class="input-section">
<h2>Enter Polygon Coordinates</h2>
<p>Click on the canvas to add points or enter them manually below.</p>
<div class="canvas-container">
<canvas id="polygon-canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas>
<button id="clear-canvas">Clear Canvas</button>
</div>
<div class="manual-input">
<div class="coordinates-container" id="coordinates-list">
<div class="coordinate-pair">
<input type="number" placeholder="X1" class="x-coord">
<input type="number" placeholder="Y1" class="y-coord">
<button class="remove-point">×</button>
</div>
</div>
<button id="add-point">Add Point</button>
</div>
<div class="units-selection">
<label for="units">Measurement Units:</label>
<select id="units">
<option value="pixels">Pixels</option>
<option value="meters">Meters</option>
<option value="feet">Feet</option>
</select>
</div>
<button id="calculate-area">Calculate Area</button>
</div>
<div class="results-section" id="results">
<!-- Results will be displayed here -->
</div>
</div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>สไตล์ CSS Create a file named styles.css for styling our calculator:
Copy * {
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
}
body {
background-color: #f5f5f5;
padding: 20px;
}
.calculator-container {
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: white;
padding: 30px;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 0 15px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
h2 {
font-size: 1.5rem;
margin-bottom: 15px;
color: #444;
}
p {
margin-bottom: 20px;
color: #666;
}
.canvas-container {
margin-bottom: 30px;
text-align: center;
}
canvas {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
.manual-input {
margin-bottom: 25px;
}
.coordinates-container {
max-height: 200px;
overflow-y: auto;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.coordinate-pair {
display: flex;
margin-bottom: 8px;
align-items: center;
}
input {
width: 80px;
padding: 8px;
margin-right: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
button {
padding: 8px 15px;
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: background-color 0.3s;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
.remove-point {
background-color: #f44336;
padding: 8px 12px;
}
.remove-point:hover {
background-color: #d32f2f;
}
#clear-canvas {
margin-top: 10px;
}
.units-selection {
margin-bottom: 25px;
}
select {
padding: 8px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.results-section {
margin-top: 30px;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f0f8ff;
border-radius: 6px;
display: none;
}
.results-section.active {
display: block;
}
.area-result {
font-size: 1.3rem;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.calculation-steps {
margin-top: 20px;
padding: 15px;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
border-radius: 4px;
font-family: monospace;
} การใช้งาน JavaScript Now, let's create the script.js file that will power our geometry area calculator :
Copy // DOM Elements
const canvas = document.getElementById('polygon-canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const clearCanvasBtn = document.getElementById('clear-canvas');
const addPointBtn = document.getElementById('add-point');
const coordinatesList = document.getElementById('coordinates-list');
const calculateBtn = document.getElementById('calculate-area');
const resultsSection = document.getElementById('results');
const unitsSelect = document.getElementById('units');
// Global Variables
let points = [];
let isDragging = false;
let dragIndex = -1;
// Canvas Setup
function setupCanvas() {
// Set canvas coordinate system (origin at center)
ctx.translate(canvas.width / 2, canvas.height / 2);
drawGrid();
// Event listeners for canvas interaction
canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', handleMouseDown);
canvas.addEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove);
canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', () => isDragging = false);
// Redraw canvas initially
redrawCanvas();
}
// Draw coordinate grid
function drawGrid() {
const width = canvas.width;
const height = canvas.height;
ctx.strokeStyle = '#e0e0e0';
ctx.lineWidth = 1;
// Vertical lines
for (let x = -width/2; x <= width/2; x += 20) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(x, -height/2);
ctx.lineTo(x, height/2);
ctx.stroke();
}
// Horizontal lines
for (let y = -height/2; y <= height/2; y += 20) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(-width/2, y);
ctx.lineTo(width/2, y);
ctx.stroke();
}
// X and Y axes (darker)
ctx.strokeStyle = '#aaa';
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
// X-axis
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(-width/2, 0);
ctx.lineTo(width/2, 0);
ctx.stroke();
// Y-axis
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(0, -height/2);
ctx.lineTo(0, height/2);
ctx.stroke();
}
// Handle mouse down event on canvas
function handleMouseDown(e) {
const rect = canvas.getBoundingClientRect();
const scaleX = canvas.width / rect.width;
const scaleY = canvas.height / rect.height;
const canvasX = (e.clientX - rect.left) * scaleX - canvas.width / 2;
const canvasY = (e.clientY - rect.top) * scaleY - canvas.height / 2;
// Check if clicking near an existing point (for dragging)
for (let i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
const dx = points[i].x - canvasX;
const dy = points[i].y - canvasY;
const distance = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (distance < 10) {
isDragging = true;
dragIndex = i;
return;
}
}
// If not dragging, add a new point
points.push({x: canvasX, y: canvasY});
updateCoordinateInputs();
redrawCanvas();
}
// Handle mouse move event on canvas
function handleMouseMove(e) {
if (!isDragging || dragIndex === -1) return;
const rect = canvas.getBoundingClientRect();
const scaleX = canvas.width / rect.width;
const scaleY = canvas.height / rect.height;
const canvasX = (e.clientX - rect.left) * scaleX - canvas.width / 2;
const canvasY = (e.clientY - rect.top) * scaleY - canvas.height / 2;
points[dragIndex] = {x: canvasX, y: canvasY};
updateCoordinateInputs();
redrawCanvas();
}
// Redraw the canvas with all points and connections
function redrawCanvas() {
// Clear the canvas
ctx.clearRect(-canvas.width/2, -canvas.height/2, canvas.width, canvas.height);
// Redraw the grid
drawGrid();
if (points.length === 0) return;
// Draw the polygon
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(points[0].x, points[0].y);
for (let i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
ctx.lineTo(points[i].x, points[i].y);
}
// Connect back to the first point if we have at least 3 points
if (points.length >= 3) {
ctx.lineTo(points[0].x, points[0].y);
// Fill the polygon with a semi-transparent color
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.2)';
ctx.fill();
}
// Draw the polygon outline
ctx.strokeStyle = '#4CAF50';
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
ctx.stroke();
// Draw the points
for (let i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(points[i].x, points[i].y, 5, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fillStyle = '#4CAF50';
ctx.fill();
// Label the points
ctx.fillStyle = '#333';
ctx.font = '12px Arial';
ctx.fillText(`P${i+1}`, points[i].x + 8, points[i].y - 8);
}
}
// Update the coordinate inputs based on canvas points
function updateCoordinateInputs() {
// Clear all existing inputs
coordinatesList.innerHTML = '';
// Add new inputs for each point
for (let i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
const pair = document.createElement('div');
pair.className = 'coordinate-pair';
const xInput = document.createElement('input');
xInput.type = 'number';
xInput.className = 'x-coord';
xInput.placeholder = `X${i+1}`;
xInput.value = Math.round(points[i].x);
xInput.dataset.index = i;
const yInput = document.createElement('input');
yInput.type = 'number';
yInput.className = 'y-coord';
yInput.placeholder = `Y${i+1}`;
yInput.value = Math.round(points[i].y);
yInput.dataset.index = i;
const removeBtn = document.createElement('button');
removeBtn.className = 'remove-point';
removeBtn.textContent = '×';
removeBtn.dataset.index = i;
pair.appendChild(xInput);
pair.appendChild(yInput);
pair.appendChild(removeBtn);
coordinatesList.appendChild(pair);
// Event listeners for manual input changes
xInput.addEventListener('change', updatePointFromInput);
yInput.addEventListener('change', updatePointFromInput);
removeBtn.addEventListener('click', removePoint);
}
}
// Update a point from manual input
function updatePointFromInput(e) {
const index = parseInt(e.target.dataset.index);
const value = parseFloat(e.target.value);
if (isNaN(value)) return;
if (e.target.className === 'x-coord') {
points[index].x = value;
} else {
points[index].y = value;
}
redrawCanvas();
}
// Remove a point
function removePoint(e) {
const index = parseInt(e.target.dataset.index);
points.splice(index, 1);
updateCoordinateInputs();
redrawCanvas();
}
// Add a new point via button
function addNewPoint() {
// Add a new point at (0, 0) or near the last point if one exists
if (points.length > 0) {
const lastPoint = points[points.length - 1];
points.push({x: lastPoint.x + 20, y: lastPoint.y + 20});
} else {
points.push({x: 0, y: 0});
}
updateCoordinateInputs();
redrawCanvas();
}
// Clear all points
function clearCanvas() {
points = [];
updateCoordinateInputs();
redrawCanvas();
resultsSection.style.display = 'none';
}
// Calculate area using the Shoelace formula
function calculatePolygonArea(vertices) {
if (vertices.length < 3) return 0;
let area = 0;
const n = vertices.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const j = (i + 1) % n;
area += vertices[i].x * vertices[j].y;
area -= vertices[j].x * vertices[i].y;
}
return Math.abs(area / 2);
}
// Display the calculation results
function displayResults() {
if (points.length < 3) {
alert("You need at least 3 points to calculate area.");
return;
}
const area = calculatePolygonArea(points);
const selectedUnit = unitsSelect.value;
let unitSymbol = 'px²';
let convertedArea = area;
// Apply unit conversions if needed
if (selectedUnit === 'meters') {
unitSymbol = 'm²';
// Assuming 1 pixel = 0.01 meter for example
convertedArea = area * 0.0001;
} else if (selectedUnit === 'feet') {
unitSymbol = 'ft²';
// Assuming 1 pixel = 0.0328 feet
convertedArea = area * 0.001;
}
// Format the result
const formattedArea = convertedArea.toFixed(2);
// Create the result HTML
let resultHTML = `
<h2>Calculation Results</h2>
<div class="area-result">
<strong>Polygon Area:</strong> ${formattedArea} ${unitSymbol}
</div>
<p>Based on ${points.length} vertices</p>
<div class="calculation-steps">
<h3>Calculation Steps:</h3>
<p>Using the Shoelace formula: A = 0.5 × |∑(xᵢyᵢ₊₁ − xᵢ₊₁yᵢ)|</p>
<ol>
`;
// Add the calculation steps
for (let i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
const j = (i + 1) % points.length;
const term = (points[i].x * points[j].y - points[j].x * points[i].y).toFixed(2);
resultHTML += `<li>Step ${i+1}: (${points[i].x} × ${points[j].y}) - (${points[j].x} × ${points[i].y}) = ${term}</li>`;
}
resultHTML += `
</ol>
<p>Summing all steps and taking absolute value: ${Math.abs(area).toFixed(2)}</p>
<p>Dividing by 2: ${(Math.abs(area)/2).toFixed(2)}</p>
</div>
`;
resultsSection.innerHTML = resultHTML;
resultsSection.style.display = 'block';
resultsSection.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' });
}
// Initialize the application
function init() {
setupCanvas();
// Event listeners
clearCanvasBtn.addEventListener('click', clearCanvas);
addPointBtn.addEventListener('click', addNewPoint);
calculateBtn.addEventListener('click', displayResults);
}
// Start the app when the page loads
window.addEventListener('load', init);การแสดงภาพว่าสูตรเชือกผูกรองเท้าคำนวณพื้นที่ของรูปหลายเหลี่ยมอย่างไร
ทำความเข้าใจกับองค์ประกอบสำคัญ มาทำลายองค์ประกอบหลักของเครื่องคิดเลขพื้นที่เรขาคณิตของเรากันเถอะ:
การโต้ตอบผ้าใบ เครื่องคิดเลขของเราใช้องค์ประกอบ Canvas HTML สำหรับการสร้างรูปหลายเหลี่ยมแบบโต้ตอบผู้ใช้สามารถ:
คลิกที่ผืนผ้าใบเพื่อเพิ่มคะแนน ลากจุดที่มีอยู่เพื่อปรับตำแหน่ง ดูการสร้างภาพข้อมูลรูปหลายเหลี่ยมแบบเรียลไทม์ ดูกริดพิกัดสำหรับการอ้างอิง ผ้าใบถูกตั้งค่าด้วยระบบพิกัดที่ (0,0) อยู่ตรงกลางทำให้ใช้งานง่ายสำหรับผู้ใช้ในการทำงานกับพิกัดทั้งบวกและเชิงลบ
ประสานงานการจัดการอินพุต ผู้ใช้สามารถป้อนพิกัดได้สองวิธี:
อินพุตภาพ: คลิกโดยตรงบนผืนผ้าใบเพื่อวางจุด อินพุตด้วยตนเอง: ป้อนพิกัดที่แน่นอนในฟิลด์อินพุต วิธีการอินพุตทั้งสองได้รับการซิงโครไนซ์ทำให้ทั้งการจัดวางภาพที่ใช้งานง่ายและอินพุตตัวเลขที่แม่นยำ
การใช้งานอัลกอริทึมเชือกผูกรองเท้า แกนกลางของเครื่องคิดเลขของเราคือการใช้สูตรเชือกผูกรองเท้า:
Copy function calculatePolygonArea(vertices) {
if (vertices.length < 3) return 0;
let area = 0;
const n = vertices.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const j = (i + 1) % n;
area += vertices[i].x * vertices[j].y;
area -= vertices[j].x * vertices[i].y;
}
return Math.abs(area / 2);
}ฟังก์ชั่นนี้:
ใช้อาร์เรย์ของพิกัดจุดยอด วนรอบแต่ละจุดและจุดถัดไป (ล้อมรอบไปยังจุดแรก) ใช้การคำนวณข้ามผลิตภัณฑ์ ใช้ค่าสัมบูรณ์และหารด้วย 2 เพื่อรับพื้นที่สุดท้าย ความงามของอัลกอริทึมนี้คือมันใช้ได้กับรูปหลายเหลี่ยมใด ๆ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นนูนหรือเว้าตราบใดที่มันไม่ได้ตัดกันตัวเอง
การเพิ่มคุณสมบัติขั้นสูง ตอนนี้เรามีเครื่องคิดเลขขั้นพื้นฐานทำงานให้ขยายด้วยคุณสมบัติขั้นสูงบางอย่าง:
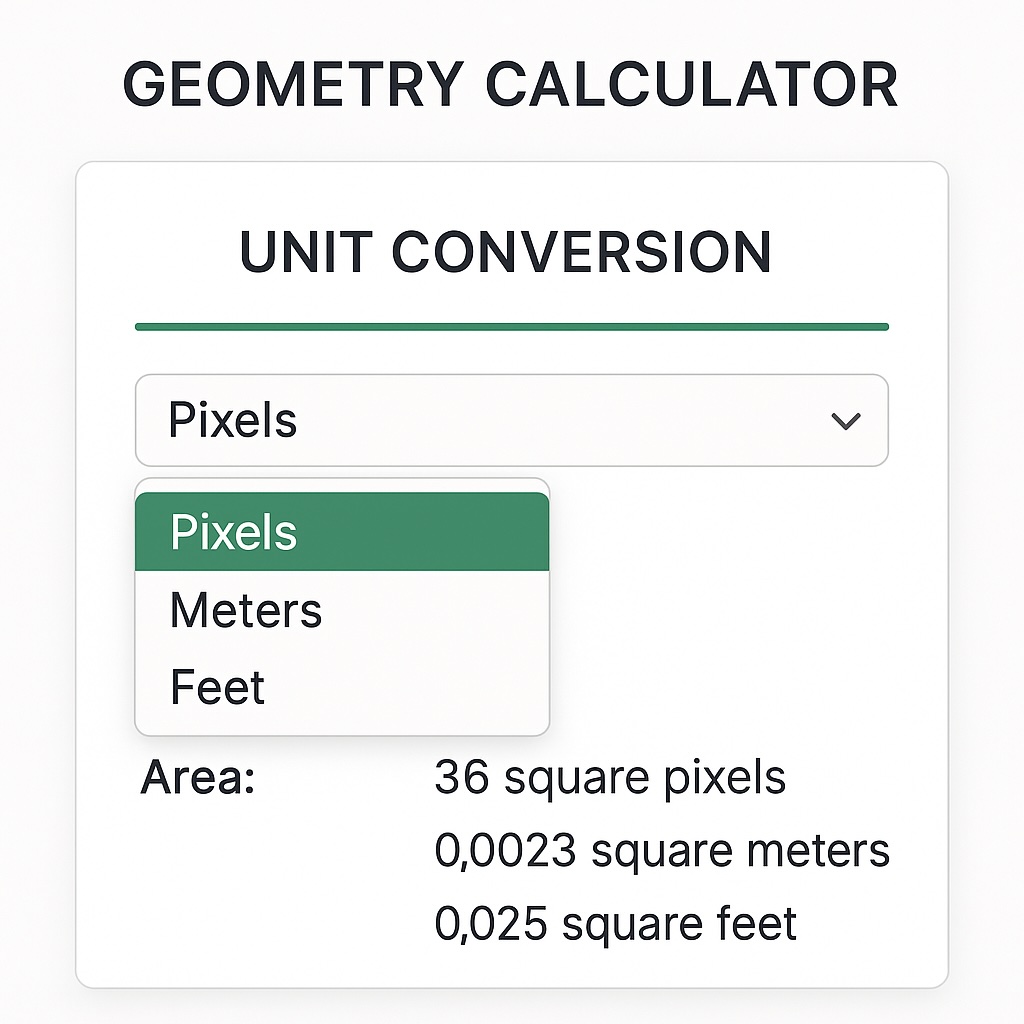
การแปลงหน่วย เครื่องคิดเลขของเรารองรับหน่วยการวัดที่แตกต่างกัน:
พิกเซล: สำหรับการวัดบนหน้าจอ เมตร: สำหรับการวัดตัวชี้วัดในโลกแห่งความเป็นจริง เท้า: สำหรับการวัดของจักรวรรดิ การแปลงหน่วยจะถูกนำไปใช้หลังจากการคำนวณพื้นที่:
Copy // Apply unit conversions if needed
if (selectedUnit === 'meters') {
unitSymbol = 'm²';
// Assuming 1 pixel = 0.01 meter for example
convertedArea = area * 0.0001;
} else if (selectedUnit === 'feet') {
unitSymbol = 'ft²';
// Assuming 1 pixel = 0.0328 feet
convertedArea = area * 0.001;
}คุณสามารถปรับแต่งปัจจัยการแปลงตามข้อกำหนดเฉพาะของคุณ
ส่วนต่อประสานเครื่องคิดเลขแสดงตัวเลือกการแปลงหน่วยสำหรับระบบการวัดที่แตกต่างกัน
ขั้นตอนการคำนวณโดยละเอียด เพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้เข้าใจวิธีการคำนวณพื้นที่เราจัดทำรายละเอียดขั้นตอนการคำนวณโดยละเอียด:
Copy // Add the calculation steps
for (let i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
const j = (i + 1) % points.length;
const term = (points[i].x * points[j].y - points[j].x * points[i].y).toFixed(2);
resultHTML += `<li>Step ${i+1}: (${points[i].x} × ${points[j].y}) - (${points[j].x} × ${points[i].y}) = ${term}</li>`;
}ความโปร่งใสนี้ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ตรวจสอบผลลัพธ์และเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับหลักการทางคณิตศาสตร์ที่อยู่เบื้องหลังการคำนวณพื้นที่รูปหลายเหลี่ยม
การทดสอบและการตรวจสอบ ก่อนที่จะพิจารณาเครื่องคิดเลขเรขาคณิตของเราให้เสร็จสิ้นให้ทดสอบด้วยรูปร่างที่รู้จักกันเพื่อตรวจสอบความถูกต้อง:
กรณีทดสอบ 1: สี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้า สี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้าที่เรียบง่ายพร้อมจุดยอดที่ (0,0), (100,0), (100,50) และ (0,50) ควรมีพื้นที่ 5,000 ตาราง
กรณีทดสอบ 2: สามเหลี่ยม รูปสามเหลี่ยมที่มีจุดยอดที่ (0,0), (50,100) และ (100,0) ควรมีพื้นที่ 5,000 ตาราง
กรณีทดสอบ 3: รูปหลายเหลี่ยมผิดปกติ รูปหลายเหลี่ยมที่ผิดปกติที่มีจุดยอดที่ (0,0), (50,100), (100,50), (75,25) และ (25,25) ควรให้พื้นที่ที่ถูกต้องตามสูตรเชือกผูกรองเท้า
สำหรับแต่ละกรณีทดสอบเครื่องคิดเลขของเราควร:
อนุญาตให้อินพุตง่ายของพิกัดทดสอบ คำนวณพื้นที่ที่ถูกต้อง แสดงขั้นตอนการคำนวณสำหรับการตรวจสอบ เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพสำหรับอุปกรณ์มือถือ เพื่อให้เครื่องคิดเลขเรขาคณิตของเราตอบสนองได้อย่างสมบูรณ์เราสามารถเพิ่มการปรับปรุงต่อไปนี้:
สัมผัสการสนับสนุนสำหรับการโต้ตอบของผ้าใบ เค้าโครงตอบสนองที่ปรับให้เข้ากับขนาดหน้าจอที่แตกต่างกัน อินเทอร์เฟซที่ง่ายขึ้นสำหรับหน้าจอขนาดเล็ก การเพิ่มเติมเหล่านี้ทำให้มั่นใจได้ว่าเครื่องคิดเลขของเราสามารถใช้งานได้บนสมาร์ทโฟนและแท็บเล็ตทำให้ผู้ใช้สามารถเข้าถึงได้ในทุกอุปกรณ์
การปรับปรุงเพิ่มเติม เพื่อให้เครื่องคิดเลขพื้นที่เรขาคณิตของเราแข็งแกร่งยิ่งขึ้นลองใช้คุณสมบัติเพิ่มเติมเหล่านี้:
รูปร่างที่ตั้งไว้ล่วงหน้า เพิ่มปุ่มเพื่อสร้างรูปร่างทั่วไปอย่างรวดเร็วเช่น:
สี่เหลี่ยม สี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้า สามเหลี่ยม วงกลม (ประมาณเป็นรูปหลายเหลี่ยมปกติ) รูปหลายเหลี่ยมปกติ (เพนตากอน, หกเหลี่ยม ฯลฯ ) การคำนวณพื้นที่สำหรับวงกลม ขยายเครื่องคิดเลขเพื่อจัดการพื้นที่วงกลมโดยใช้:
Copy function calculateCircleArea(radius) {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}การคำนวณปริมณฑล เพิ่มฟังก์ชันการทำงานเพื่อคำนวณขอบเขตของรูปหลายเหลี่ยม:
Copy function calculatePolygonPerimeter(vertices) {
let perimeter = 0;
const n = vertices.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const j = (i + 1) % n;
const dx = vertices[j].x - vertices[i].x;
const dy = vertices[j].y - vertices[i].y;
perimeter += Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
return perimeter;
}การประหยัดและโหลดรูปหลายเหลี่ยม ใช้งาน LocalStorage เพื่อบันทึกและโหลดการกำหนดค่ารูปหลายเหลี่ยม:
Copy // Save polygon
function savePolygon(name) {
const polygonData = JSON.stringify(points);
localStorage.setItem(`polygon_${name}`, polygonData);
}
// Load polygon
function loadPolygon(name) {
const polygonData = localStorage.getItem(`polygon_${name}`);
if (polygonData) {
points = JSON.parse(polygonData);
updateCoordinateInputs();
redrawCanvas();
}
} แอปพลิเคชันที่ใช้งานได้จริง แอพพลิเคชั่นในโลกแห่งความเป็นจริงที่หลากหลายซึ่งเครื่องคำนวณพื้นที่เรขาคณิตให้บริการโซลูชั่นที่มีคุณค่า
เครื่องคิดเลขพื้นที่เรขาคณิต JavaScript ของเรามีแอพพลิเคชั่นที่ใช้งานได้จริง:
การพัฒนาเว็บ แผนที่แบบโต้ตอบและการสร้างภาพพล็อต แอปพลิเคชันการสำรวจที่ดิน เครื่องมือวางแผนอสังหาริมทรัพย์ เค้าโครงห้องพักและแอพพลิเคชั่นการออกแบบ การศึกษา การสอนหลักการเรขาคณิตแบบโต้ตอบ การแสดงแนวคิดทางคณิตศาสตร์ การสร้างแหล่งข้อมูลการเรียนรู้แบบโต้ตอบ การพัฒนาเกม การตรวจจับการชนสำหรับวัตถุเกม การออกแบบระดับและการสร้างสิ่งแวดล้อม การสร้างขั้นตอนการสร้างโลกของเกม บทสรุป ในบทช่วยสอนที่ครอบคลุมนี้เราได้สร้างเครื่องคิดเลขพื้นที่เรขาคณิตที่ทรงพลังและมีประสิทธิภาพโดยใช้ JavaScriptเครื่องคิดเลขของเราสามารถ:
คำนวณพื้นที่ของรูปหลายเหลี่ยมใด ๆ โดยใช้สูตรเชือกผูกรองเท้า จัดเตรียมอินเทอร์เฟซภาพที่ใช้งานง่ายสำหรับการสร้างและแก้ไขรูปร่าง สนับสนุนอินพุตพิกัดคู่มือสำหรับการวัดที่แม่นยำ แปลงระหว่างหน่วยการวัดที่แตกต่างกัน แสดงขั้นตอนการคำนวณโดยละเอียดเพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ทางการศึกษา หลักการและเทคนิคที่เราได้กล่าวถึง - เรขาคณิตแบบประสาน, อัลกอริทึมเชือกผูกรองเท้า, การจัดการผ้าใบและการออกแบบส่วนต่อประสานผู้ใช้ - เป็นทักษะที่มีค่าซึ่งขยายเกินกว่าโครงการนี้คุณสามารถนำไปใช้กับความท้าทายในการพัฒนาเว็บที่หลากหลายตั้งแต่การสร้างภาพข้อมูลไปจนถึงแอปพลิเคชันแบบโต้ตอบ
ด้วยการสร้างเครื่องคิดเลขเรขาคณิตนี้คุณไม่เพียงสร้างเครื่องมือที่มีประโยชน์ แต่ยังทำให้คุณเข้าใจแนวคิดทางคณิตศาสตร์และการใช้งานใน JavaScriptอย่าลังเลที่จะขยายเครื่องคิดเลขด้วยคุณสมบัติเพิ่มเติมเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพประสิทธิภาพหรือรวมเข้ากับโครงการของคุณเอง
การเข้ารหัสมีความสุข!
ทรัพยากรสำหรับการเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติม